|
|
 |
| Support this site |
| |
|
| |
BT 21CN & the ISP Network - WBC/WBMC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This page provides an overview of how an ISP's network joins BTs 21st Century Network. On previous pages there's an overview of BTs 21st Century Network FAQs and BT's 21CN network topology, which covers transmission of data from the home, to the exchange and over BTs core network. The traditional IPStream and DataStream products will gradually be withdrawn and replaced by a totally new wholesale products.
Its up to the ISP to decide which product they use, they may if they wish use a combination of both. We will look at the ISP options shortly, but first we will look at the products available to the End User - which is the customer like you and me.
~ WBC/WBMC End User Product Set. Below is the list of products currently available for customers of those ISPs who provide services via the 21CN backhaul.
WBC is the base product for Internet Service Providers which all other wholesale variants are based upon. It's product set is not quite the same as previous products which offered rental of VPs at the exchange (Datastream) or IPStream where the ISPs could connect using a central pipe at a central location. In the future BTw are looking to use SRA and adding Annex M.
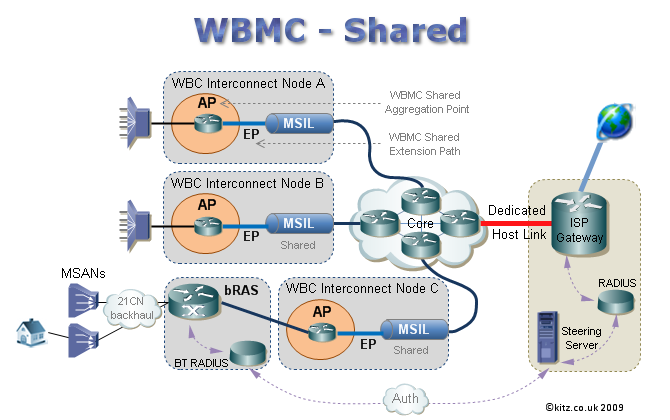
Wholesale Broadband Managed Connect (WBMC) is a product aimed at small to medium sized ISPs /CPs for whom it would be economically unviable to purchase their own MSILs. WBMC is transported over the MPLS core which is owned & managed by BTw and presented to the ISP as single 10 Mbps - 1Gbps host link. 10Gbps host links are also planned for the future. With WBMC it is BT Wholesale who is responsible for managing and purchasing the AP, EP and MSIL which is then shared by multiple ISPs and charged accordingly.
BTw is responsible for the WBC transportation of traffic from the customer's home, exchange backhaul and on to & over the core. Meaning that the ISP only has to purchase a single host link at any one of the core locations for all of their customers - regardless of where they are in the UK. Thus providing an affordable solution for smaller ISPs. This is similar to the older IPStream Centrals.
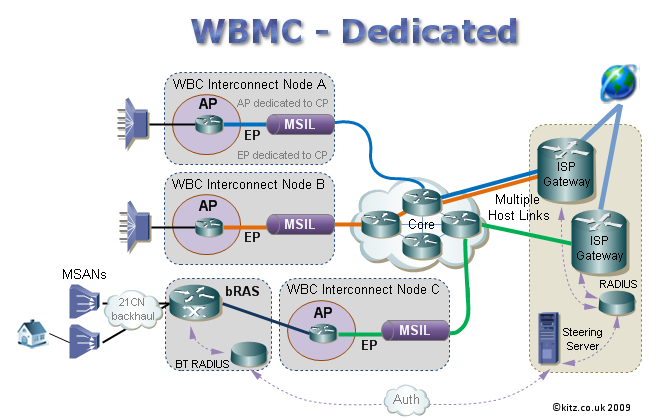
Dedicated WBMC is aimed at medium to large sized CPs/ISPs who have a high concentration of customers at each of the core nodes. BTw figures suggest > 300k-500k at core nodes. The WBC network has 20 core nodes which the ISP may connect to. The CP/ISP is responsible for the purchase of bandwidth on the MSIL which can be 1Gb or 10Gb links. The ISP can effectively manage their network and independently purchase the required amount of bandwidth needed at each location.
Traffic from the AP via the MSIL is then routed via the core to the ISP's gateway or their PoP of choice, giving the ISP the option of routing regional traffic to regional gateways or just one location.
WBC, Dedicated WBMC & Shared WBMC in a nutshell At this point if you are still wondering what is the difference is between Shared WMBC, Dedicated WBMC and WBC? In simple terms the answer is:-
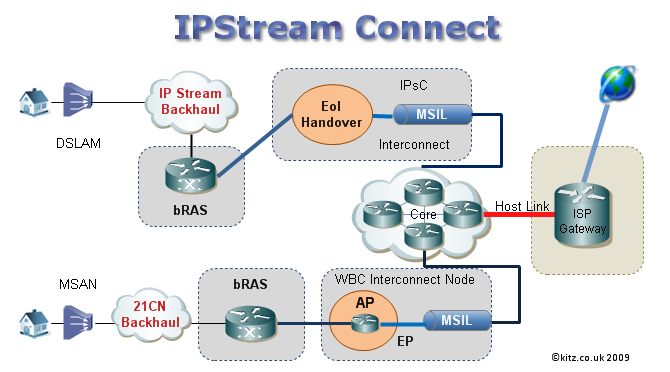
~ What is IPStream Connect (IPsC)? IPStream Connect is intended as a transition product for IPStream ISPs during the roll out nationwide of 21CN. IPStream Connect is not 21CN in that it only offers adsl1 (up to 8Mb) rather than adsl2+ (up to 24Mb). Instead it is a way for IPStream ISPs to connect customers whose exchanges have not yet been upgraded to 21CN, by allowing the ISP to take traffic at the bRAS on to either their own or a 3rd party backhaul. The users broadband connection is routed in the normal way from home <-> exchange <-> RAS over the IPStream backhaul. Once at the RAS, the interconnect will form a new Equivalence of Input (EoI) point. From here traffic can either be handed over to a third party network, or routed on to the BTw core network that is used by 21CN until it reaches the ISP gateway.
The theory behind IPStream Connect is that ISPs to consolidate IPStream and 21CN customers within one platform. It is envisioned that IPStream, DataStream and IPStream Connect with gradually be withdrawn from 2014 as more exchanges are upgraded to 21CN and ISP centrals are gradually replaced by WBC/WBMC.
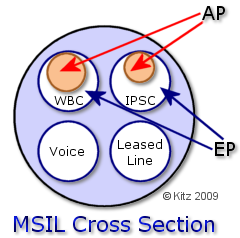
~ What are Aggregation Points (AP)? An AP or Aggregation Point is a convergence point on a WBC Interconnect Node that combines traffic for a destination. To expand further the AP is an access port on a BEA (Broadband Edge Aggregator), which will likely be a Juniper Edge Router. Think of the Aggregation Point as being the physical access point to and from the BT backhaul where traffic merges for all customers being served from that area - kind of like a reverse ISP home gateway, its the gateway to the BTw backhaul heading back to the exchange. An ISP using WBC or Dedicated WBMC will purchase 'x' amount of bandwidth at an AP for use by their customers whose connections aggregate at that particular core node. If it helps you could think of the AP as like purchasing bandwidth for the old central, the difference being that bandwidth is only used by customers coming off that particular core node, rather than from anywhere in the UK. With WBC the AP is the point where congestion can occur if the ISP hasn't purchased enough bandwidth. BT monitors traffic going through the AP and if the ISP goes over their contracted allowance, the ISP can either elect to pay a premium for 'over use age' or only allow the contracted amount of bandwidth to pass through, which is when users will start to see the effects of contention. It would appear that BT are currently allowing ISPs some lea way for excess usage: In the case of shared WBMC, BTw provides the AP and the bandwidth is shared by all customers of all WBMC ISPs using that particular AP.
~ What is an Extension Path (EP)? An EP or Extension Path officially is the link between the AP and the MSIL. A WBC ISP has to purchase 'y' amount of EP bandwidth. Extension Path bandwidth could be though of as reserve bandwidth for growth, as the eventual aim is that EP bandwidth will at some point in the future be utilised. ISP's planning for future growth may for example have an EP of 500Mb, but only have a 300Mb AP. As the ISP grows then they can gradually increase the bandwidth on the Aggregation Point up to the size of the Extension Path. If it helps, you could perhaps think of the EP being like an old 622Mb central pipe where the ISP could light 155Mb sections at a time. The difference is that the amounts of the AP and EP are designated by the ISP up to the size of the MSIL they purchase. WBCs will pay BT for both contracted AP bandwidth and a lesser amount for the 'unused' EP bandwidth. One of the main differences between APs, EPs & centrals though is that if an ISP reaches capacity on their AP, they can go over this amount and into the EP reserve. BT charges a hefty premium though for any ISP dipping into EP bandwidth that is over their contracted AP bandwidth. In this instance the EP could be thought of as similar to a bank overdraft.
~ MSIL, AP & EP - How they fit together.
Steering is telling BTw which ISP gateway the customer should connect to. When a customer logs on to their internet connection, the BT system identifies which ISP the customer belongs to and looks up the IP address of the gateway that they should connect via from the ISP maintained steering server. Steering is used on both WBC and WBMC, but works slightly differently on each system.
ISPs maintain the records of customers details such as the BBEU -v- connecting location gateway IPs on their steering servers.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All rights reserved
Unauthorised reproduction prohibited
|
|
|
|