All ISPs run their networks slightly differently as the amount of
capacity and requirements will vary depending upon their type of users.
BT Wholesale offer a service called Central Plus whereby BTw do the
majority of the routing for ISPs and takes customers of these ISP's
adsl traffic straight out to the Internet. Customers of ISPs that
use Central Plus will see BT routing before their ISP details when
they do a tracert.
Larger ISPs tend to lease Central Pipes from BT, so that they can
route and manage users traffic themselves.
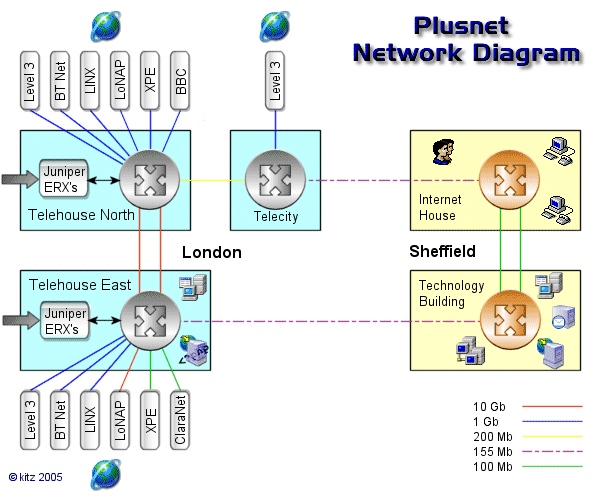
Below is a diagram of Plusnet's network. The diagram is interactive
- move your mouse over various points to identify the equipment and
a link to more information about the equipment.
BT Central Pipes
Generic Information on BT Central Pipes can be found on my page How
adsl works 2.
Current information on Plusnet's Central Pipes in use can be found
on its own page here.
Edge Routers
These powerful routers terminate the ISP end of the Central
and control the traffic flow in and out of the internet.
Plusnet currently have 6 Juniper ERX 1440's and 1 x E320 and are the first
hop you will see when performing a tracert.
These Junipers act as the aggregation point where service providers
accept and authenticate connections for tens of thousands of
customers. The E-series allows authenticated users access only
to the bandwidth, QoS, services and features that they have
subscribed to. Therefore, it is the key place in the network
to control, deliver and account for customer services.
Each 14-slot Router contains a 40Gbps switch fabric and supports
full redundancy. 12 slots are dedicated to line modules.
A 155Mb line card on a Juniper can sustain 8000 subscribers
up to a maximum of 48,000 therefore a Juniper could take traffic
from more than a single 622 Mb pipe.
Back to Network diagram.
|

Full size images:
Front Rear
PDF
More info at juniper.net
|
Gateway routers
An ISP will have a multitude of gateway and internal routers
whose task it is to direct traffic on to the next part of our
journey.
Depending upon where you have requested data from, these routers
will pass you on to the best path to ensure that your data gets
to its destination.
Back to Network diagram. |
 |
Transit Providers
|
These are companies that specialise in forwarding data between various countries
and overseas. An ISP may use several different transit providers
for different routing. The ISP will have to pay the organisation
transit costs for data sent and received.
Well known transit providers include Level 3, BT net, Cogent,
Sprint.
Back to Network diagram.
|
 |
Colocation Centre
|
A colocation centre (or colo) is a large data centre where ISPs and other
telecommunication companies site their networking equipment
on secure premises.
These premises provide air conditioned rooms which are vital
for powerful servers and routers. They offer high standards
of security against disasters such as fire, intrusion, and power
outages.
Telehouse (North and East London) and Telecity (London and
Manchester) are 2 organisations in the UK which offer colo facilities.
Back to Network diagram.
|

Telecity London
|
Peering Points
|
Peering Points offer ISPs a point where they can exchange
traffic with each other. Peering is offered by organisations
located in a colocation centre.
The idea of peering is that ISPs can reduce their transit
costs on the internet backbone. It also has an added benefit
that it can provide a more direct access point to another ISP.
LoNAP, LINX, XchangePoint (XPE) and MaNAP are some of the companies
in the UK that offer peering services.
Back to Network diagram.
|
 |
Servers
Powerful computers that are dedicated to a specific task. An ISP
will have many different types of Servers. The server will host a
specific type of information and then "serve" the data to
the user. Some essential Servers are Mail, Web, File and database,
other types of servers that an ISP may have are dedicated games servers,
CGI servers, SQL etc.
|
|
ftp, web stats and mail servers. |
NetApp Storage Cluster |
|
Back to Network
diagram.










